Search
Hot bent glass and tempered curved glass are two different glass processing technologies, which have significant differences in processing methods, performance, and application scenarios.
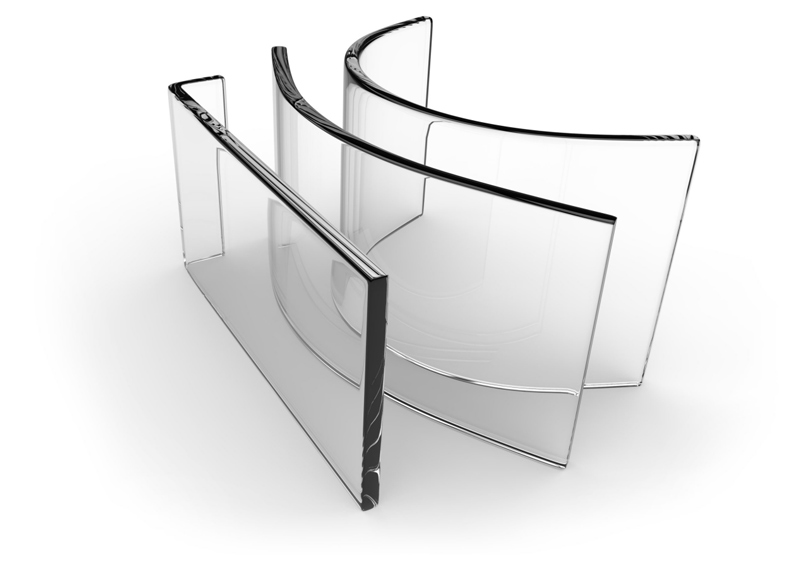

Processing method
Hot bending glass: Softened by heating at around 400 degrees Celsius, extruded into shape through a mold, then naturally cooled to complete the process. The processing of hot bent glass mainly relies on the hot bending furnace, which is convenient for temperature control and operation.
Tempered curved glass: Heating at around 700 degrees Celsius softens the glass, then naturally formed in a mold and rapidly cooled by blowing air. The tempered glass surface forms uniform compressive stress and internal tensile stress, effectively improving the hardness, strength, bending resistance, and impact resistance of the glass.
Performance differences
1, Strength and hardness: Tempered glass has four times the strength of hot bent glass, and after breaking, it splits into uniform small particles, providing higher safety.
2, Bending and impact resistance: Tempered glass of the same thickness has an impact resistance strength that is 3-5 times that of hot bending glass, and a bending strength that is also 3-5 times that of hot bending glass.
3, Thermal stability: Tempered glass has good thermal stability and can withstand temperature differences of around 200 ℃, while hot bending glass has poor thermal stability.
4, Safety: Tempered glass has undergone tempering treatment, resulting in higher safety; However, hot bent glass has not undergone tempering treatment, resulting in lower safety.
Applications
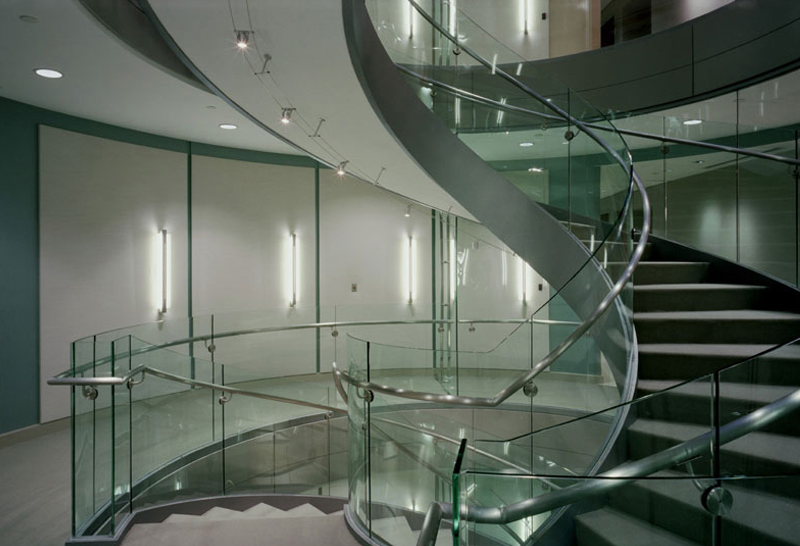
Hot bent glass: commonly used in furniture decoration, instrumentation, sightseeing elevators, transportation engineering, stair handrails and other scenes.

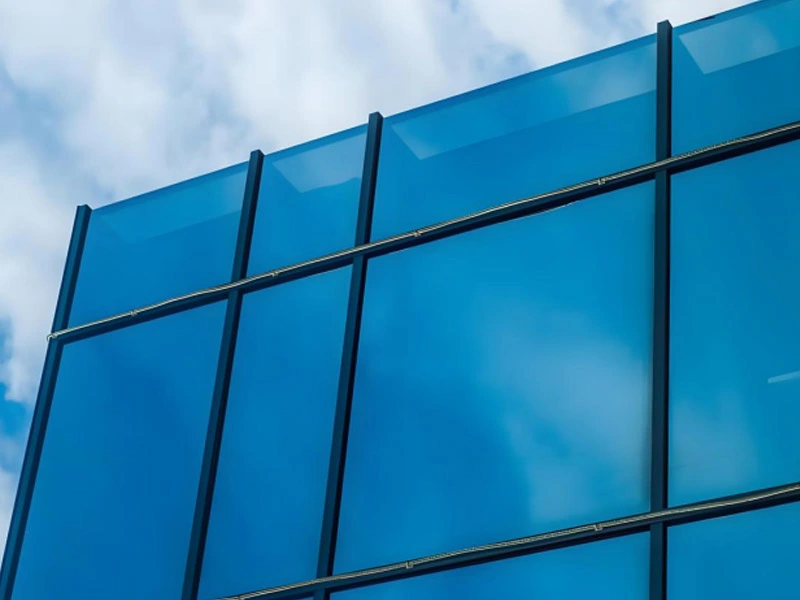
Tempered curved glass: Used for building exterior walls, canopies, sightseeing elevators, windshields of transportation vehicles, etc., it is widely used due to its high safety and impact resistance.
QUICK LINKS
Phone
+86-13505332015Address
Juyuan Road, Wangcun Town, Zibo City, Shandong Province, China