If you do not need air conditioning cooling in summer, do not need heating in winter, warm in winter and cool in summer, but also low carbon environmental protection? What do you think of?
Yes, the passive room. Let's take a look at it.
Passive houses are also called passive houses, or passive energy saving houses. Is a new energy-saving building, is no active supply of energy to meet the cooling and heating needs of the house, in short, is a highly energy efficient and comfortable livable building.

History of the passive house: The House of Hamburg
The concept of "passive house" began in 1996, the first "passive house" was built in 1999, each of 90 square meters of three bedrooms, the main wooden structure. The construction cost of this house is only 7% higher than the average house, but the operating cost is very low, the use of solar heating, power supply can be self-sufficient, in 2004, a household heating, water, electricity is only 114 euros.
energon, the world's largest passive office building, was built in Ulm, Germany, in 2002. According to the requirements published by the Darmstadt Passive House Agency, the building must meet specific criteria in terms of annual thermal demand, heat load, air density and basic energy requirements in order to be called a qualified "passive house".
The construction of passive houses is not limited by the type of building, including office buildings, housing, school buildings, sports halls and industrial buildings. Therefore, ordinary buildings can be reconstructed to meet the standard requirements of "passive house", which has extensive practical significance. More than 6,000 passive houses are currently in use in Germany, Austria, Switzerland and Italy. The "Hamburg House" is the first certified "passive house" in China.
1. The insulation layer of the external protection structure is particularly thick, the yellow part is the insulation layer, the left side is the thickness of the insulation layer of the general house, and the right side is the thickness of the insulation layer of the passive house.
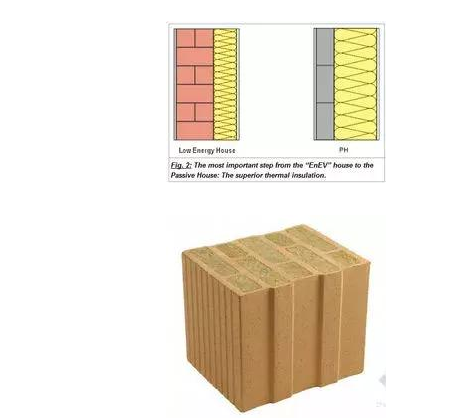
Sample of clay brick with internal cavity filled with insulation material

Passive house wall and window structure stereoscopic cutting diagram
2, super energy-saving window "passive house" required not only to reduce heat loss, but also to increase insulation and comfort. Even in cold, frosty weather, the interior side glass can exceed 17°C.
Indicators of passive house Windows:
A, Uw value ≤0.8W/(m²K)

B, Ug-1.6W /(m²K) ·g < 0, g value is generally around 0.5.
If this condition is met, It shows that the solar thermal energy obtained by passive Windows in winter is greater than the energy lost due to conduction.
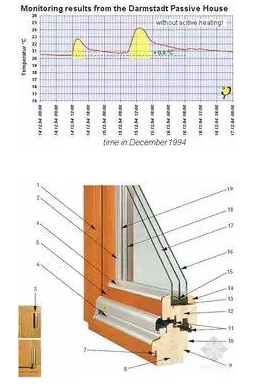
Three-dimensional cutting diagram of the three-layer glass insulation window
3. Some parts of the building envelope without thermal bridge form areas with relatively dense heat flow and low internal surface temperature under the action of indoor and outdoor temperature differences. These parts become bridges with more heat transfer, so they are called thermal bridges, and sometimes they can be called cold bridges.
The so-called thermal bridge effect, that is, the physical effect of heat conduction, because there are concrete ring beams and structural columns in the floor and corner, and concrete materials have better thermal conductivity than wall materials (the thermal conductivity of concrete materials is 2 to 4 times that of ordinary bricks), and because of poor indoor ventilation, the temperature difference between indoor and outdoor is large in late autumn and early winter, and cold and hot air frequently contact. The thermal conductivity of the wall insulation layer is not uniform, resulting in thermal bridge effect, resulting in dew, mold and even dripping on the interior wall of the house.
The thermal bridge free building structure of the passive house can avoid the occurrence of the above phenomenon.
4, good sealing in the positive and negative pressure detection, there are strict requirements for gas loss. Because if the seal is not good, hot and cold gas convection will occur, resulting in heat loss.
5, the ventilation system active ventilation (countercurrent air/air heat exchange) provides high-quality air, while using at least 75% of the waste heat of the exhaust gas to heat the pumped fresh air, at this time the exhaust gas and fresh air are not mixed. Because the passive house is very well sealed, the air change can be optimized, and it is strictly controlled at 0.4/h (air exchange rate per hour).
The outdoor fresh cold air, through the green pipe line, first enters the core control components of the indoor energy recovery ventilation system. The indoor exhaust gas containing a certain amount of heat, through the yellow pipe line, also gathers into the core control components of the indoor energy recovery ventilation system. The energy recovery ventilation system traps most of the heat in the exhaust gas and heats the fresh air entering the room. The preheated fresh air is sent to each room through blue pipe lines. After the heat recovery, the exhaust gas is discharged to the outside through the pipe line.
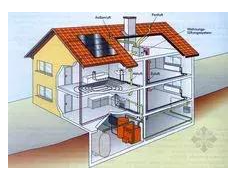
Indoor energy recovery ventilation system, solar hot water system + boiler hot water system + floor heating system + radiator heating + domestic hot water - hot water exchange storage mixed system, schematic diagram
In the future, the construction industry will definitely develop in the direction of environmental protection, energy saving and high quality. As a kind of high energy efficiency, high comfort and high quality building form, passive house will definitely occupy a place in the future.